Examples
In the following examples, the EndPoint used was an Equipment. Nevertheless, the procedure for performing Requests for other Endpoints is very similar so by following the next examples, you should be able to replicate it for other Endpoints.
Single Entity
Reading
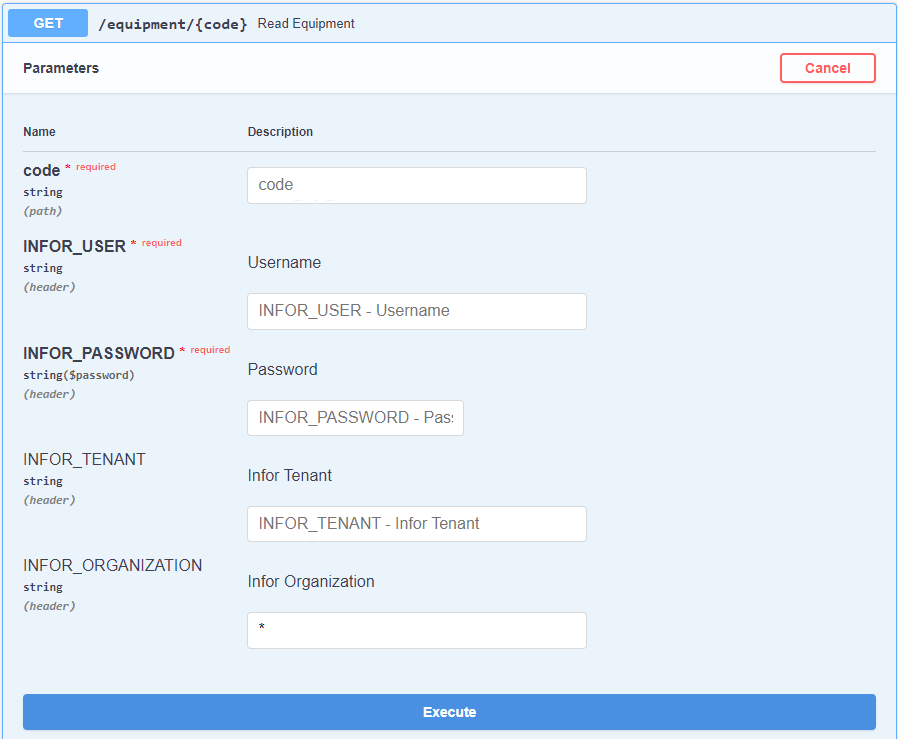
In order to read a Single Entity, the user needs to specify the Entity's Code, its CERN Username and NICE Password. The typical window requesting these informations can be seen in Figure 3. For other Endpoints, other informations might be demanded as well that the user must fill in order to send the Request.
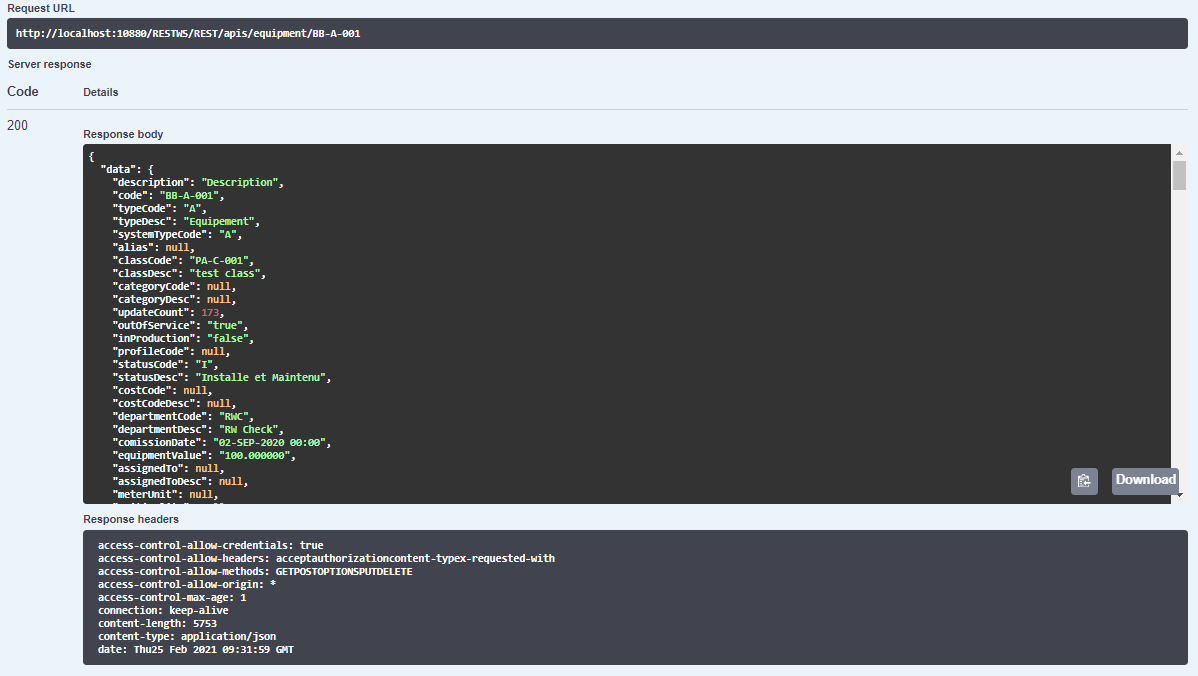
After the Request has been executed successfully, the user will see a new window with the Request URL and the Response Body with the associated Response Code. This is displayed in Figure 4.
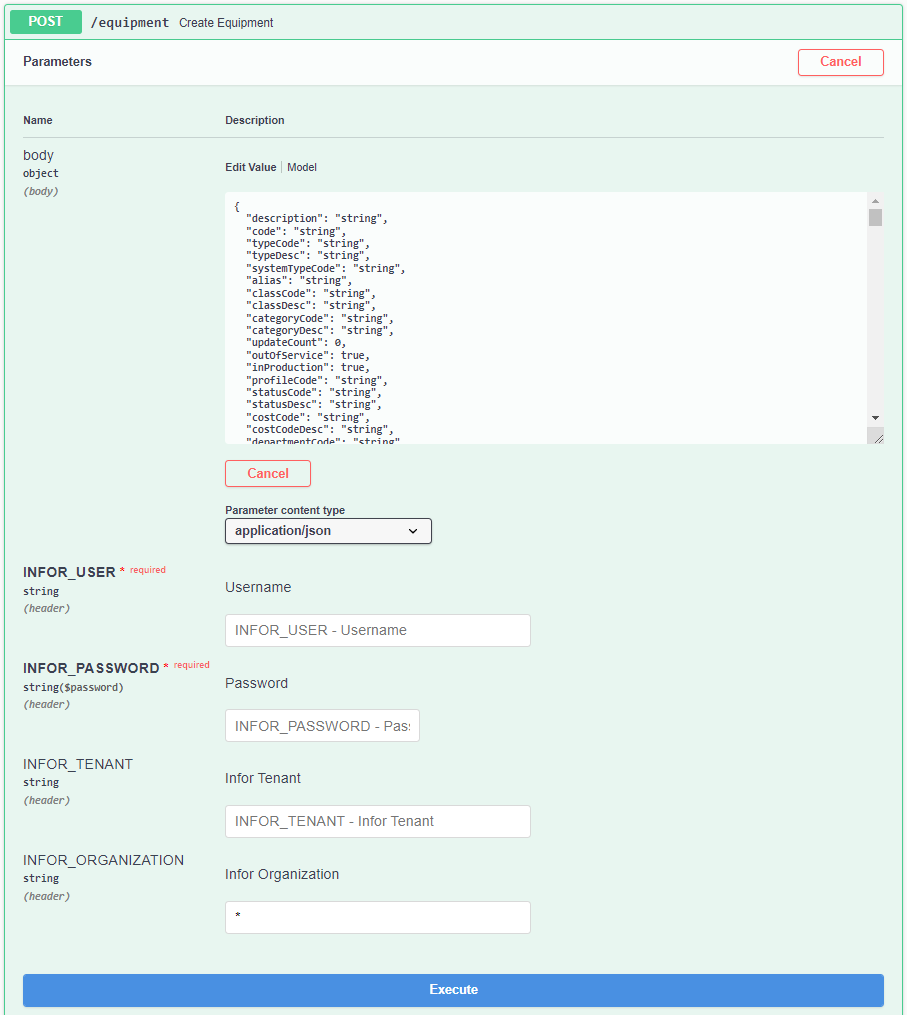
Creating
To create a Single Entity, the user only needs to specify the Entity's Code and the fields to be updated in the Request Body. If the user wants to nullify a field, it must be filled with an empty string "". The window to create the Entity can be seen in Figure 6.
If the user desires to create an Entity with Custom Fields, it is necessary to add the Custom Field to the Body and specify the Custom Field Code and the Custom Field Value, such as in the code below.
Updating
To update a Single Entity, the user only needs to provide the Entity's Code and the Fields that should be updated in the Request Body. If the user wishes to nullify a field, then it must filled with an empty string "". An example of this procedure can be seen in Figure 7.
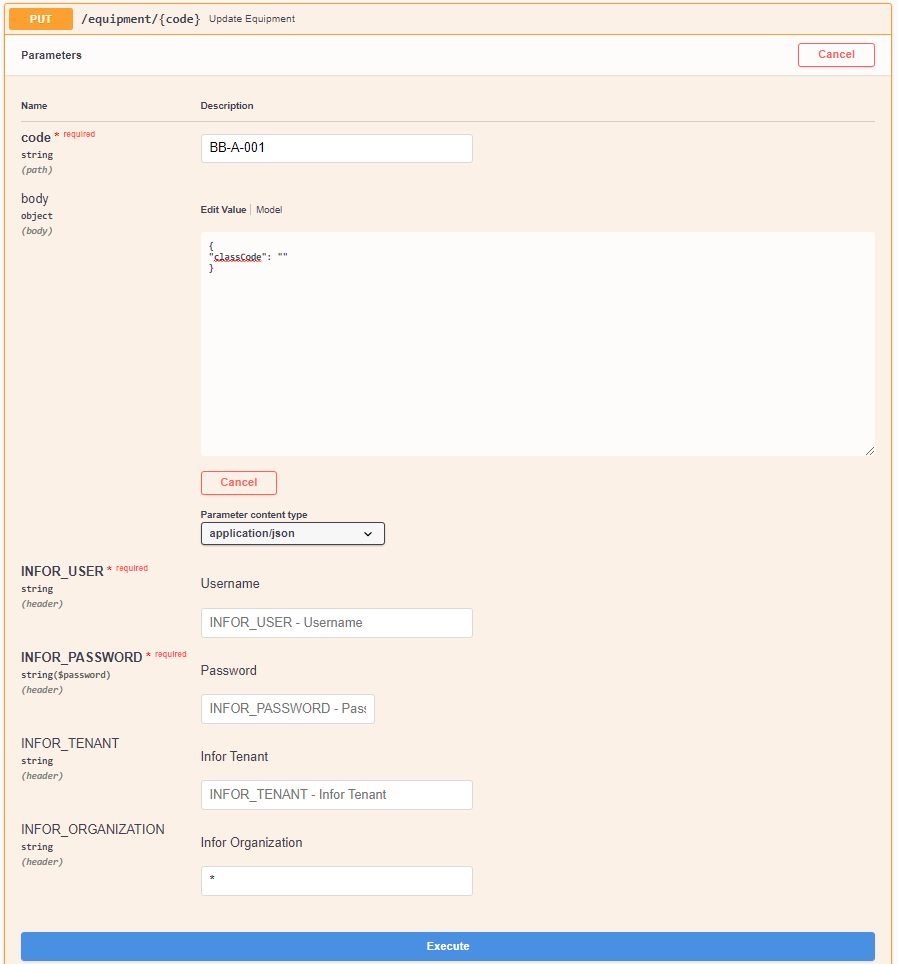
If the user wishes to update a Custom Field, then it is only needed to specify the Custom Field Code and the Custom Field Value in the Body, just like in the case of its creation.
Deleting
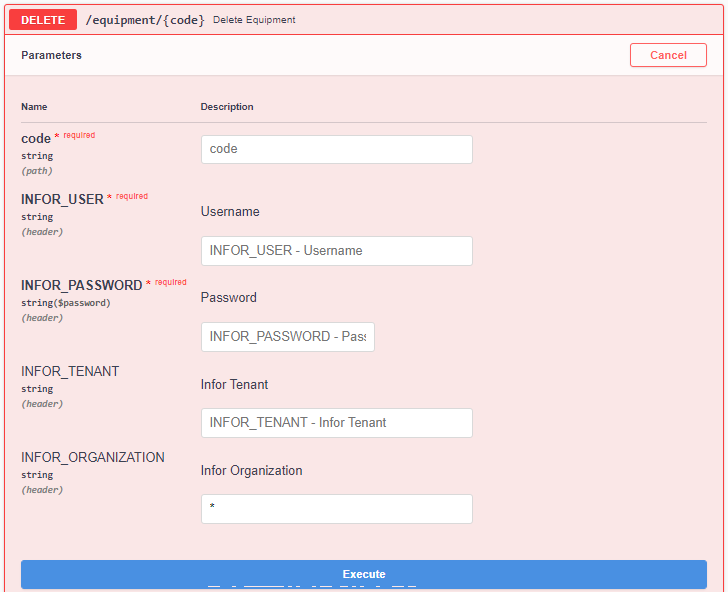
In order to delete a Single Entity, the user needs to specify the Entity's Code, its CERN Username and its NICE Password. If the user has the right permissions, then the Entity will be deleted. The window to perform this acction can be seen in Figure 8.
Multiple Entities
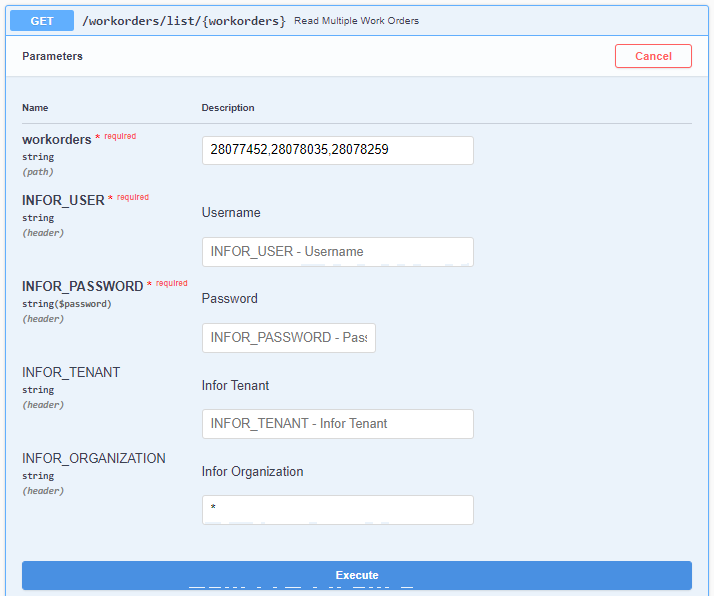
General
Some Endpoints allow to manage Multiple Entities at the same time. When managing these Multiple Entities, the different Entities need to be separated by commas ,. The remaining operations are similar to the case of Single Entities. In Figure 9, an example is shown where the user is trying to read several Work Orders at once.